We live in a fast-paced world in which advertisers race to keep up with consumer behavior and trends.
The collective attention span has drastically decreased in the last few years due to digital information overload. Consequently, more and more consumers are becoming immune to ads.
Nowadays, crafty designs or short videos often prove to sell better than traditional 30-second ads.
Promoters count on several tactics to boost the effectiveness of advertising, and most of them are related to the psychological appeal of ads, whether we talk about color and cognitive psychology or body language. 
When using specific visual advertising techniques, designers combine various elements to achieve results that are not only pleasing to the eye but also engaging to target audiences.
Here are 15 compelling advertising techniques and examples to keep you inspired:
Table of Contents
- Color Psychology
- Typographic Composition
- Minimalism
- Emotional Appeal
- Bandwagon
- Gestalt Principles
- The Golden Ratio
- The Focal Point
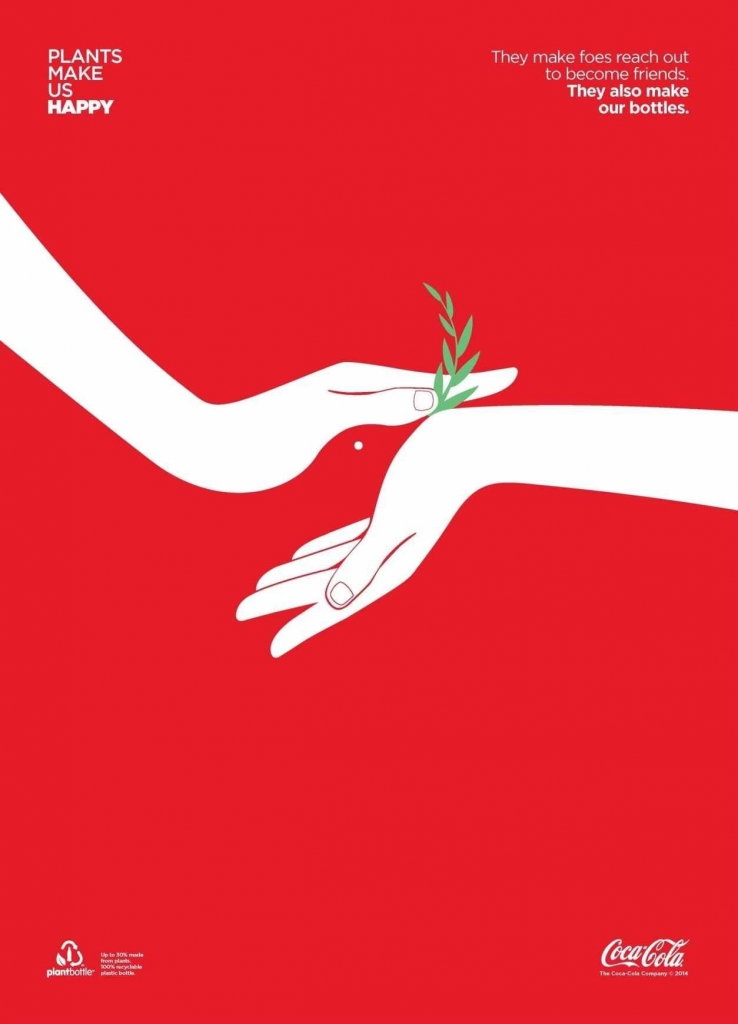
- Association
- Symbolism
- Body Language
- Endorsements
- Behind-the-Scenes
- Fantasy
- Facts and Statistics
- Humor
- Storytelling
- Influencer Marketing
- Conclusion
1. Color Psychology
It’s no secret that color psychology is one of the most common and effective techniques used in advertising.
Color psychology analyzes the influence of colors upon human behavior, decision-making, and, ultimately, purchase.
Color schemes have the power to send powerful messages without the use of too many words, as they set the tone of everything that follows.
In color psychology, every shade has a different meaning. For example, black can be used to make a product look elegant and luxurious. White can symbolize minimalism, and yellow is a universal, accessible color that brings contrast to visuals.
Take, for example, one of the latest California Market Center’s advertising campaign, in which no visual element is sloppy or neglected:

Whether you are choosing to work with complementary colors or use a single tone, bright, striking shades can stop potential customers from scrolling.
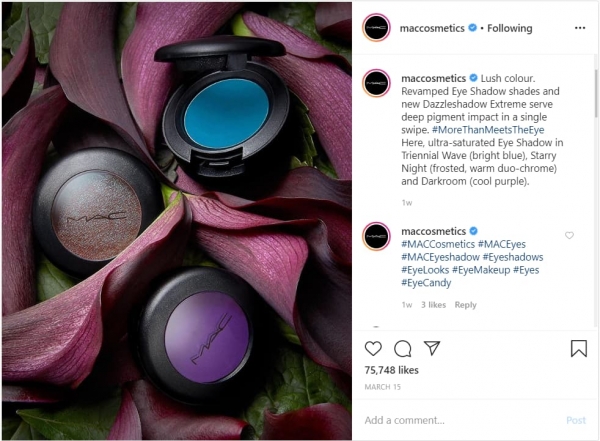
We also like this MAC Cosmetics’ Instagram post, in which they used earth tones and natural elements to advertise their latest products.
To learn more about color psychology, you can check this color graphic study by Iconic Fox.
2. Typographic Composition
Typography is an essential part of both advertising and design.
Fonts have the power of influencing the way that your audience perceives a message, as they can further depict information and make visual storytelling more effective.
When creating an ad, think about how you can pair fonts, and don’t forget to make sure that both styles are in perfect balance and complement the ad’s color palette.

3. Minimalism
Popular social media platforms, such as Facebook and Instagram, are packed with sponsored posts, and since potential customers are already engaging in various social activities, slipping your products and deals in their newsfeed is not a bad idea.
While there are many techniques that you can use to make your ads stand out, minimalism is one great visual style to get your products noticed, plus it matches the platform’s layout.
Putting your products front and center, on a white or neutral background, in a carousel ad can do the trick, not to mention the fact that you can promote more than one product with a single ad.
4. Emotional Appeal
It’s safe to say that emotionally charged ads can go straight to your audience’s heart, as the emotional appeal technique has proved to be one of the most persuasive approaches in advertising.
Advertisements that evoke human emotions, such as happiness, sadness, surprise, fear, anger, or disgust, create engaging experiences for consumers.
With the use of association and symbolism, promoters motivate potential customers to take specific actions.
There are many things to take into consideration when creating emotional ads. Yet, the most crucial aspect is to do your research well so that you can have a clear understanding of your target audience and their perceptions.

BURIBA., a Branding & Advertising Agency, launched an Instagram puzzle game on International Women’s Day to promote diverse beauty standards and empower women.
5. Bandwagon
As one of the most persuasive modern techniques, the bandwagon effect can tap into what your audience desires, using emotional cues to make people act quickly when purchasing something.
One approach is to advertise the fact that you have a series of limited products that your audience needs to buy right away.
In other words, this ad technique relies on FOMO, also known as the fear of missing out.
The hip clothes brand Supreme is the king of bandwagon ads, and their strategy is to create a single batch of products and items that are usually sold at high prices, for a limited amount of time.
But does this technique really work?
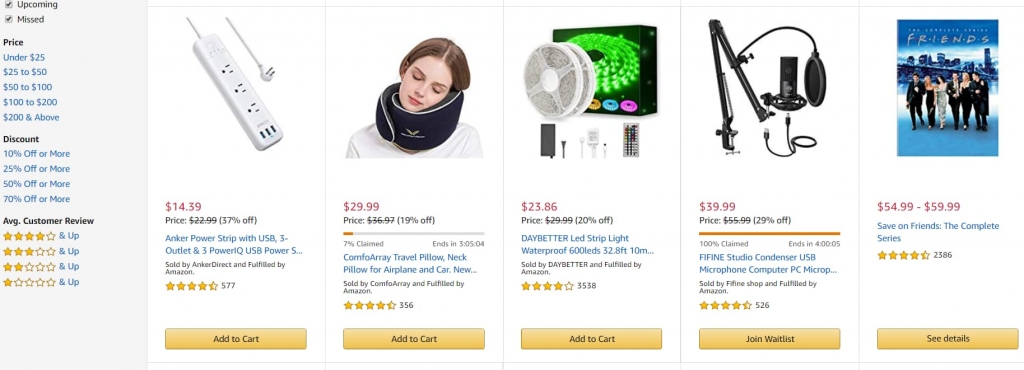
Amazon is the ultimate testimonial for the Bandwagon approach, as the platform obviously goes the extra mile to match potential customers who have similar needs, with their listings.
Plus, the online retail giant sets limited timeframes for sales and allow people to put themselves on waitlists for high demand products.
6. Gestalt Principles
This principle is as German as it gets—everything has to run smoothly, and all elements have to be carefully positioned in design.
The Gestalt Principles are a set of laws describing how the human brain works and how we perceive the world from a design perspective, helping visual content makers to build more engaging experiences.
For a better understanding, let’s take a quick look at eight of these principles:
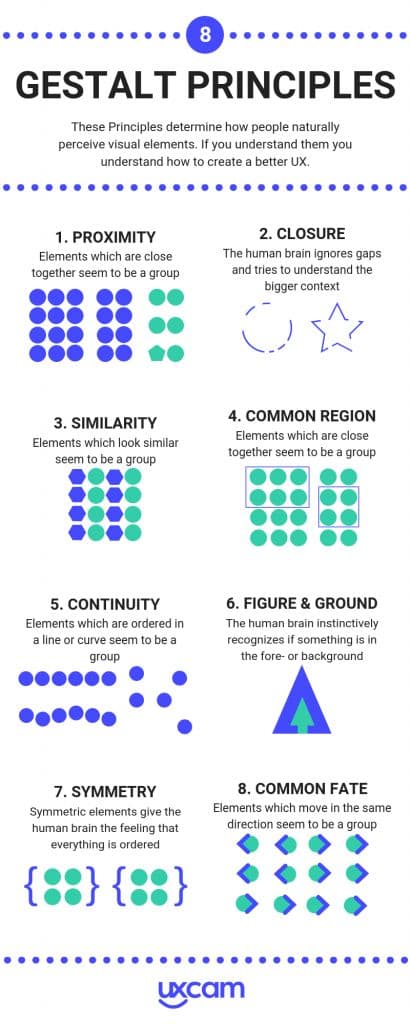
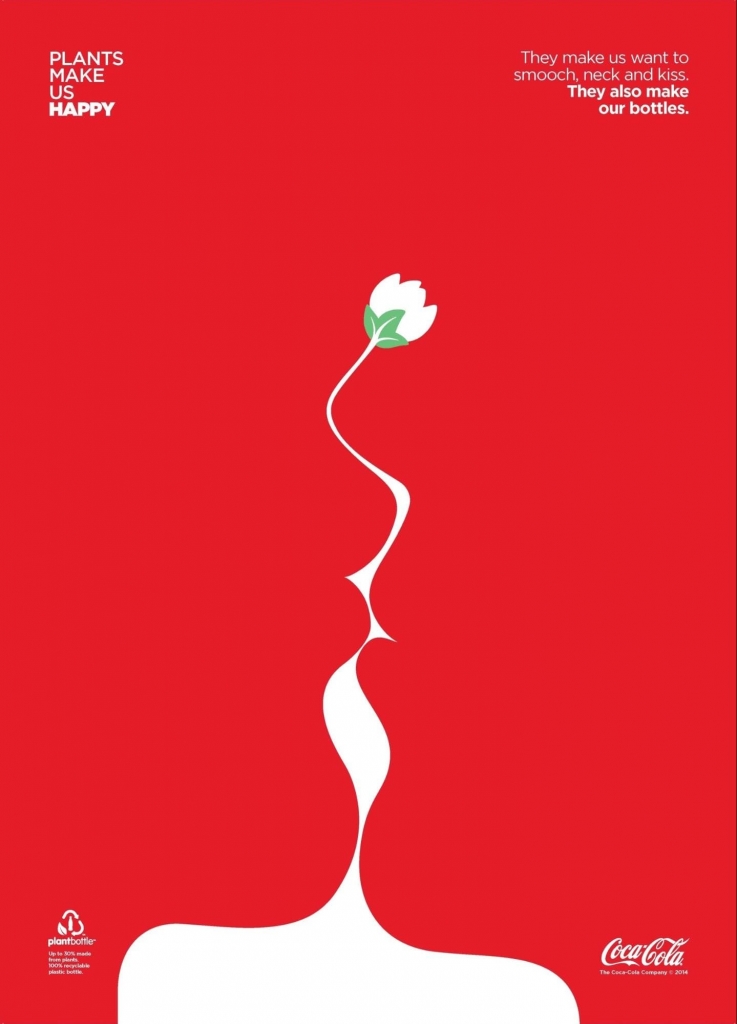
If you’re wondering how big-league brands like Coca-Cola are using Gestalt principles, below is an exemplification:
7. The Golden Ratio
Designers, take note: this is the mathematical ratio encountered everywhere in nature, and used in design it creates perfect compositions, that are not only effective but also remarkably pleasing to the eye.
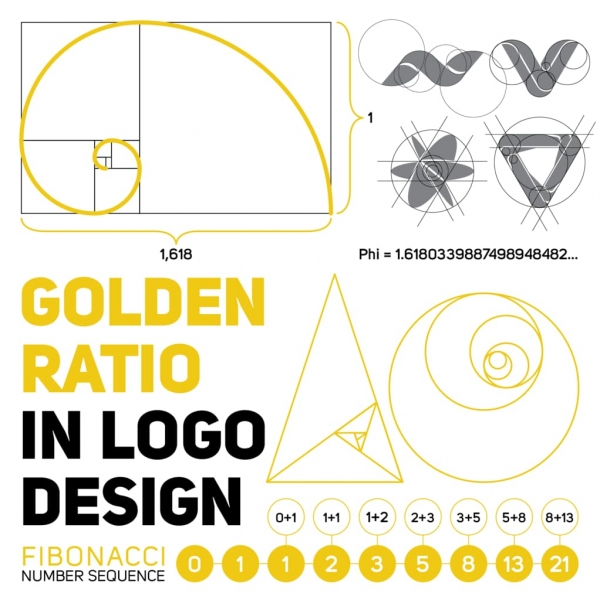
The Fibonacci numbers can be used as an advertising technique as well. Potential clients are more likely to notice ads with an airy approach method.
Ultimately, the idea is that all ads should stand on balanced elements, and most importantly, have a similar focal point. Keep the Golden Ratio in mind when sketching the actual design, and you’ll impress potential customers in no time.

*This ad was created with Creatopy
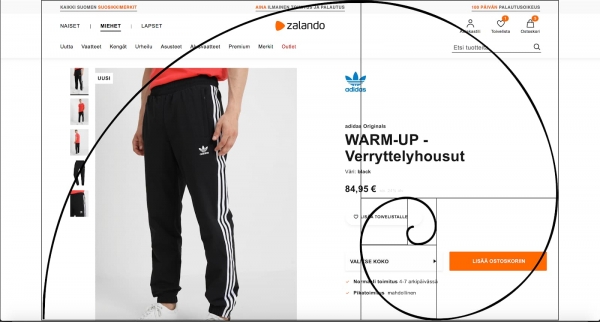
8. The Focal Point
Among the techniques of visualization in advertising, there is the focal point method.
Although this principle is also part of the Golden Ration approach, it’s just as important as the choice of colors or fonts. Through this technique, the ad sets the scene and creates a distinctive spot for the audience to look at.
Take, for example, this campaign for Happy Meal’s 40th anniversary.

They created a landscape where kids left all of their toys on the floor, along with a Happy Meal.
The M shaped line that goes straight into the box can symbolize the way kids jump all day till the point they’re starving, and the line also creates a focal point for the ad.
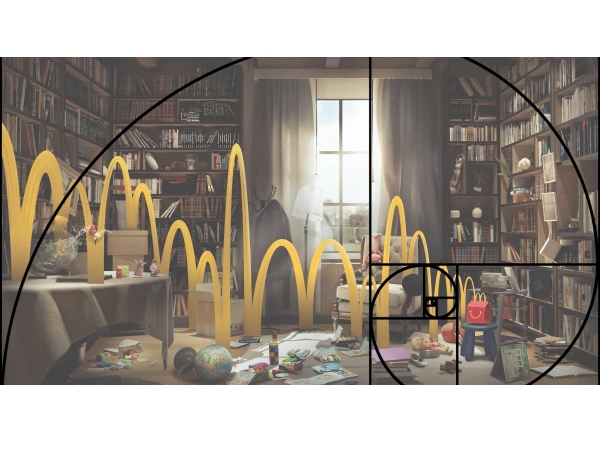

*created with Creatopy
9. Association
Appealing once again to human psychology, this method uses images to create a whole chain of ideas and thoughts behind a design.
One luxurious item, like an expensive watch, can make people think they have a luxurious life, and on the same note, some brands are associated with a particular lifestyle.
Evian, for example, used this principle to suggest their water is safe for toddlers.
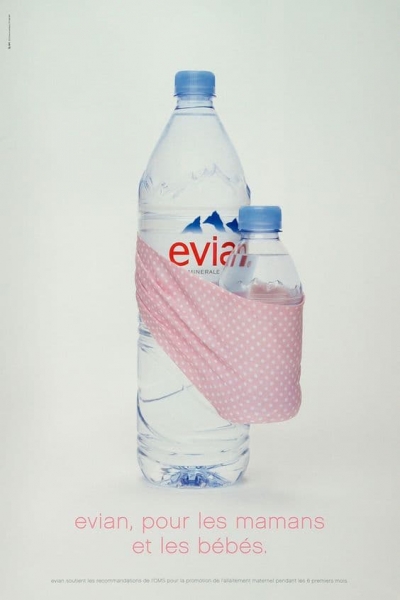

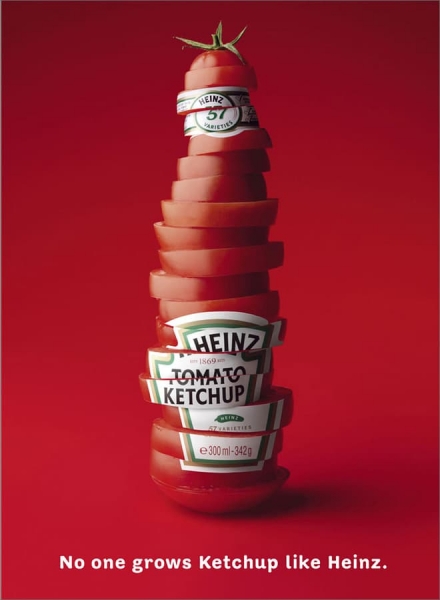
10. Symbolism
This is another visual technique that relies on the use of symbols in advertising and is very similar to the one that we explained above. Symbolism uses dramatic visuals, metaphors, or similarities to draw attention and interest towards a product.
Take this ad from Heinz as an example.
The ketchup bottle took the shape of sliced tomatoes, and they also added a catchphrase at the end to exhibit the product’s quality.
11. Body Language
Sometimes, instead of using text to convey the message, advertising works with body language, a nonverbal form of communication. By using this strategy, your ad can express emotions through a person’s posture, body movement, or any other form of facial expression.
A subcategory of the body language technique is gaze induction. What this means is that the person featured in the ad (usually a celebrity in a perfume or luxury brand watch ad) will not be looking directly at the viewer, creating a feeling of mystery.
Below you can see a representative example.
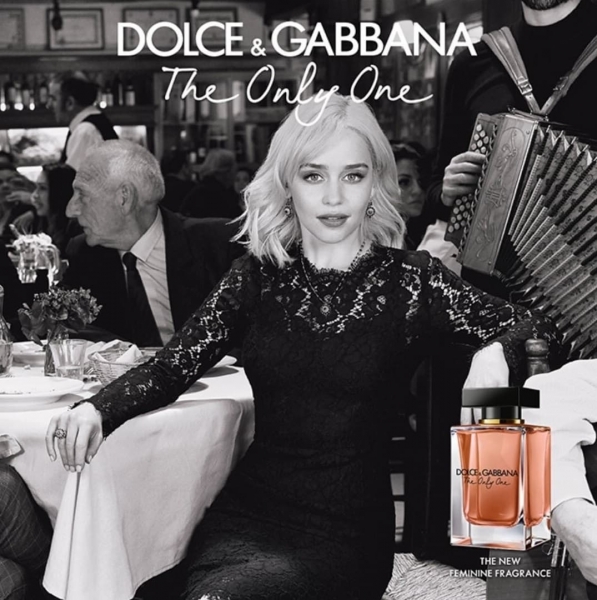

And in this one from Dior, you can see the Three-Quarter Gaze in action.

12. Endorsements
The previous visual ad technique takes us directly to this one. Certain brands use celebrities for advertising their products because they carry a particular influence over their audience.
Consumers want to use the same perfume as their favorite celebrity. Women are more likely to buy makeup products used by a personality they’re influenced by. Active people want to work out in the same type of shoes as their favorite basketball player, and the list goes on.
And the best news? Millennials have a soft spot for endorsements.

According to this article, Matthew McConaughey increased sales for Lincoln, so this technique can be effective for luxury brands.
And since we mentioned makeup products, one example is Rita Ora being the face for Rimmel London. The beauty company teamed up with her and launched a line of signature products, such as lipsticks and nail polish.

13. Behind-the-Scenes
Among the various types of advertising methods, this one always works when you want your audience to feel more connected to your brand.
Photos and videos from behind the scenes will make your customers appreciate the hard work that went behind a campaign.
Take this Apple HomePod ad, for example:
And this is the behind-the-scenes video.
An elaborate video like this showing the bits and pieces of advertising can impress some people.
Take a look below at Breitling’s behind-the-scenes video with John Travolta.
14. Fantasy
Another strategy in advertising is the use of fantasy. The combination of the advertised product and a fantastic visual element never ceases to spark the audience’s imagination.
Through this creative ad, the brand wants to let potential customers know that the car can provide safety, even during winter.

15. Facts and Statistics
The usage of facts and statistics is a popular technique used in promotion.
They can be persuasive by calling out the rational part of the human brain. Personally, I’d say that this technique comes in handy for selling cosmetics or house cleaning products.
Here’s how Nivea used this technique in one of their ads.

And here’s an example from Dettol.

16. Humor
Using humor in advertising can turn ordinary promotional messages into enjoyable, memorable, and highly shareable content. By incorporating humor into their campaigns, brands can grab the audience’s attention and create a lasting impression that goes beyond a typical advertisement. The success of a humorous ad depends on its ability to connect with the audience’s sense of humor while staying true to the brand’s identity and message
Old Spice’s “The Man Your Man Could Smell Like” campaign used humor to revitalize the brand and appeal to younger audiences. The campaign, featuring absurd scenarios delivered with deadpan humor by Isaiah Mustafa, went viral and demonstrated how humor can effectively engage and entertain while conveying the brand’s message.

17. Storytelling
Storytelling in advertising involves creating a narrative that captivates the audience’s attention and conveys the brand’s message in a relatable and engaging way. A well-crafted story can elicit emotional responses, making the brand more memorable and impactful.
Apple’s advertising often emphasizes storytelling to highlight how its products enhance the lives of its users. For example, the “Shot on iPhone” campaign showcases real stories and moments captured by everyday users, emphasizing the product’s quality and the brand’s connection to creativity and innovation.

18. Influencer Marketing
In today’s digital age, influencer marketing has become a powerful advertising strategy. Influencers are individuals with a large following on social media who have the ability to influence the opinions and purchasing decisions of their audience. Brands partner with influencers to create genuine and compelling content that promotes their products.
Gymshark collaborates with fitness influencers and athletes to showcase workout routines, fitness tips, and personal stories while wearing Gymshark apparel. Influencers such as Nikki Blackketter and Steve Cook contribute to the brand’s credibility and outreach, fostering trust and boosting engagement with Gymshark’s target audience.
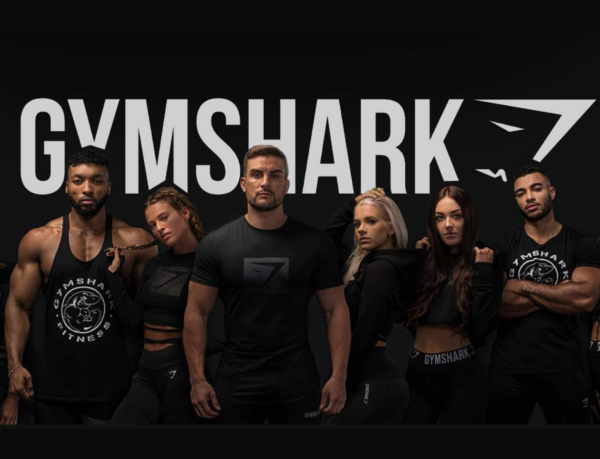

19. Conclusion
Despite the constant change in digital advertising, these strategies and techniques are likely to be just as effective in the future.
As long as you stay well aware of your target audience, identifying the best techniques to draw their attention should be an achievable goal. Never stop experimenting with various approaches, and make sure to do your best to keep potential customers interested in the products that you’re promoting.
Did you use any of these techniques in your ad creation process? Let us know in the comments section below!